Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nihei, Naoto*; Yoshimura, Kazuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Katengeza, E.*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Ochi, Kotaro; Iimoto, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
The rate of temporal change of radiocesium concentration in bottom sediments is governed not only by its physical decay but also by various ecological processes. In this study, the decreasing trend of radiocesium concentration over wide pond areas of surface sediments (up to 10 cm depth), due to ecological processes, was investigated using plastic scintillation fibers (PSF) and was quantified by the ecological half life. PSF measurements were conducted between 2013 and 2019. Their conversion factors ((Bq/kg)/cps) were obtained by comparison between detected radiation counting rate obtained by PSF and the concentration of radiocesium in sediment cores collected from coinciding positions within the same ponds. A forest catchment pond exhibited the longest ecological half life and may indicate catchment derived radiocesium input as was partly evident in the spatial temporal patterns of radiocesium concentration at this pond's inlet.
 Cs dissolution from dam lake sediment considering temperature and dissolved oxygen condition
Cs dissolution from dam lake sediment considering temperature and dissolved oxygen conditionTsuji, Hideki*; Hayashi, Seiji*; Higashi, Hironori*; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Funaki, Hironori; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Suzuki, Takashi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Misono, Toshiharu; Dohi, Terumi; Mino, Yoshihisa*; Sukigara, Chiho*; Ito, Yukari*; Kanda, Jota*; Ishimaru, Takashi*
no journal, ,
A time-series sediment trap was deployed from October 2017 to June 2018 at a station located in southeast of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant to clarify the transport process of suspended radiocesium from the coast to the offshore area. Sinking particles of 39 periods were collected by this experiment. Radiocesium was detected from sinking particles throughout the observation period, and the concentration showed clear seasonal variation. The observed flux of radiocesium showed maxima in winter (December-January) and spring (March-April). From detailed analysis of physical and chemical characteristics of sinking particles, it was found that sinking particles were composed of biological particles with relatively low degradation in winter and fine-grained terrestrial particles in spring. Especially in spring, high radiocesium flux was observed, and it was presumed due to lateral transport of radiocesium-bound lithogenic particles from the coastal area to the offshore. However, the effect of redistribution of radiocesium in seabed sediments by this process is considered to be limited.

 C,
C, 
 N)
N)Tanaka, Sota; Kakinuma, Hotaru*; Adachi, Taro*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun
no journal, ,
Terrestrial arthropods could be an indicator species of long-term behavior of radiocesium through the food chain due to their large biomass and importance as food resources for other organisms. The spider, Nephila clavata, as generalist predators is especially suggested that an indicator species of radiocesium contamination of insect communities because they prey on variety of food resources from both grazing and detrital food chain. In present study, the aggregated transfer factor (T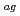 ) of
) of  Cs for the spiders inhabited at mountainous forest and riverside was calculated using the initial deposition densities map, and stable isotope ratio(
Cs for the spiders inhabited at mountainous forest and riverside was calculated using the initial deposition densities map, and stable isotope ratio(
 C,
C, 
 N) of the spider was measured to determine the transfer pathway of
N) of the spider was measured to determine the transfer pathway of  Cs.
Cs.
Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Dohi, Terumi; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
Development of more reliable sorption reaction model is essential for estimating a behavior of radionuclide migration in the environment, which contributes to the safety assessment of waste disposal of contaminated soil and wastes. Observation by various spectroscopic methods is helpful to understand a chemical condition of metal ions sorbed on soil and host rock surface. The TEM-EELS and TEM-EDS methods were used in the present study. These have been applied to lighter elements, while very few studies for heavier metals. Therefore, Eu and Zr as analogs of tri and tetravalent actinides were examined. After attaching powder samples on a copper grid, a thin layer of carbon was deposited to prevent charge-up. No peak except zero loss in the spectrum was obtained for Eu oxide, since the particle size was too large and the electron transmission in the sample might be suppressed. The EDS peaks of Zr(acac)4 were clearly observed, and also small sharp peaks in EELS were observed at the edges of Zr and O.
Nakanishi, Takahiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Funaki, Hironori; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Miura, Tomisato*; Yoshida, Mitsuaki*
no journal, ,
To elucidate the mechanism of transport of dissolved radiocesium to masu trout, a feeding experiment was conducted in a culture pond introduced with mountain stream water (dissolved  Cs concentration: 0.1 - 0.2 Bq/L) using a non-contaminated bait. The
Cs concentration: 0.1 - 0.2 Bq/L) using a non-contaminated bait. The  Cs concentration in the muscle of the adult masu trout (n = 10) was relatively high, showing individual differences (30 - 200 Bq/kg-wet). Pond bottom gravel was found in their stomach, suggesting a source of
Cs concentration in the muscle of the adult masu trout (n = 10) was relatively high, showing individual differences (30 - 200 Bq/kg-wet). Pond bottom gravel was found in their stomach, suggesting a source of  Cs other than bait and stream water. As a result of dietary analysis using stable isotope ratios, the contribution of aquatic organisms was higher in masu trout with higher
Cs other than bait and stream water. As a result of dietary analysis using stable isotope ratios, the contribution of aquatic organisms was higher in masu trout with higher  Cs concentration in the muscle. This suggests that the
Cs concentration in the muscle. This suggests that the  Cs concentration in masu trout does not exceed the Japanese limit of 100 Bq/kg for general foodstuffs by transport only from the dissolved
Cs concentration in masu trout does not exceed the Japanese limit of 100 Bq/kg for general foodstuffs by transport only from the dissolved  Cs.
Cs.
Tagomori, Hisaya*; Kawamura, Hidehisa*; Kusano, keiichi*; Dohi, Terumi
no journal, ,
To investigate their spatial distribution and physicochemical properties of the radiocaesium-bearing micro particles (CsMPs), an efficient methodology for determine and analysis them is required. Here we focused on CsMPs from litters as they may affect the radiocaesium cycling in forest ecosystem. In this study we developed a method to determine CsMPs (mostly 1-10  m sizes) from litters by combine digestion treatment and automatic particle analysis with FE-EPMA. In total it took up to 3 days for detecting one CsMP from huge amounts of mineral-like and metallic particles. In the ToF-SIMS analysis for Cs isotope ratios of CsMPs to understand their emission source as the next step, pretreatment for easily detecting micron-sized samples is needed. To solve this problem, FIB technique was used for Gallium marking formation around target sample. Preliminary Cs isotope ratios(133Cs, 134(Cs + Ba), 135Cs, 137(Cs + Ba)) and their distributions of CsMPs were determined by applying these approaches. We developed pretreatment for microscopy and ToF-SIMS analysis of CsMPs.
m sizes) from litters by combine digestion treatment and automatic particle analysis with FE-EPMA. In total it took up to 3 days for detecting one CsMP from huge amounts of mineral-like and metallic particles. In the ToF-SIMS analysis for Cs isotope ratios of CsMPs to understand their emission source as the next step, pretreatment for easily detecting micron-sized samples is needed. To solve this problem, FIB technique was used for Gallium marking formation around target sample. Preliminary Cs isotope ratios(133Cs, 134(Cs + Ba), 135Cs, 137(Cs + Ba)) and their distributions of CsMPs were determined by applying these approaches. We developed pretreatment for microscopy and ToF-SIMS analysis of CsMPs.
Saito, Takumi*; Fukuoka, Masafumi*; Fujiwara, Kenso
no journal, ,
Environmental behaviors of radioactive Cs is crucial to predict long-term changes of its distribution in soil or river environments. It is known that Cs is selectively bound to micaceous minerals in nature and inert for chemical exchange reactions. Nevertheless, dynamics of labile fractions of Cs in a given environment if any must play an important role for its environmental behaviors, as it directly contributes to the mobility and bioavailability of Cs. In this study, we perform in-situ evaluation of the labile Cs in soil and aqueous environments of Fukushima Prefecture by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT), which is a technique designed for the lability measurement of trace elements in nature. In river environments exceeds the dissolved ones, suggesting that the desorption of Cs from suspended particles modulates its behaviors in river water. Meanwhile, in soils we have found that the distribution of the labile fraction of radioactive Cs is heterogeneous with particulate materials rich in labile Cs and that the proportion of the labile Cs in a soil column becomes large at the depth deeper than 5 cm from the surface.
 Cs discharge characteristics from a forested catchment of the Ohta River
Cs discharge characteristics from a forested catchment of the Ohta RiverSakuma, Kazuyuki; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Funaki, Hironori; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Ochi, Kotaro; Hayashi, Seiji*; Tsuji, Hideki*; Ozaki, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
Cesium-137 leaching from decomposing forest litter is thought to be one pathway by which dissolved  Cs enters rivers from forests. To clarify whether this process contributes or not, we studied the correlation between humin-like matter from microorganism-induced plants decomposition and dissolved
Cs enters rivers from forests. To clarify whether this process contributes or not, we studied the correlation between humin-like matter from microorganism-induced plants decomposition and dissolved  Cs concentrations. River water samples were collected approximately once a month from April 2017 to August 2019 at 10 locations (7 locations from April 2019) from the upstream of the Ohta River in the Namie and Minamisoma districts. These samples were filtered through 0.45-
Cs concentrations. River water samples were collected approximately once a month from April 2017 to August 2019 at 10 locations (7 locations from April 2019) from the upstream of the Ohta River in the Namie and Minamisoma districts. These samples were filtered through 0.45- m-pore size membrane filters. The dissolved
m-pore size membrane filters. The dissolved  Cs concentrations and fluorescence intensities of humin-like matter were measured. A positive correlation was found between the fluorescence intensities of humin-like matter and normalized dissolved
Cs concentrations and fluorescence intensities of humin-like matter were measured. A positive correlation was found between the fluorescence intensities of humin-like matter and normalized dissolved  Cs concentration (R
Cs concentration (R = 0.17, p
= 0.17, p  0.001). The results indicate that
0.001). The results indicate that  Cs leaching from forest litter because of litter decomposition can contribute to increasing the dissolved
Cs leaching from forest litter because of litter decomposition can contribute to increasing the dissolved  Cs concentration in river water in forested catchments.
Cs concentration in river water in forested catchments.
Taniguchi, Keisuke*; Takeuchi, Yukio*; Fujita, Kazuki*; Dohi, Terumi; Hayashi, Seiji*; Kuramoto, Takayuki*; Nomura, Naoki*; Aono, Tatsuo*
no journal, ,
In Fukushima Prefecture, although decontamination has been completed except for difficult-to-return areas, most of the forest has not been decontaminated yet. From the forest, radiocaesium may enter rivers and affect downstream areas. A survey was conducted in three forested watersheds of the Nanokazawa, Saruta, Nuno rivers located in Fukushima Prefecture to understand the amount and characteristics of radiocaesium flowing out. In each watershed, suspended solids (SS) were collected by a suspended sand sampler, water was collected every few months, and the water level and flow rate were measured. After freeze-drying the SS sample, the concentration of suspended Cs-137 was measured by a germanium semiconductor detector. The water sample was filtered through a membrane filter with a pore size of 0.45  m, then the dissolved Cs-137 was collected by the solid-phase extraction disk method or AMP coprecipitation method, and the dissolved Cs-137 concentration was measured by a germanium semiconductor detector. The ranges of dissolved Cs-137 concentration in FY2019 were 69-190 mBq/L in the Saruta River, 9.7-16 mBq/L in the Nanokazawa river, and ND-3.2 mBq/L in the Nuno River. In the poster, we will also present the results of SS measurements and flow observations.
m, then the dissolved Cs-137 was collected by the solid-phase extraction disk method or AMP coprecipitation method, and the dissolved Cs-137 concentration was measured by a germanium semiconductor detector. The ranges of dissolved Cs-137 concentration in FY2019 were 69-190 mBq/L in the Saruta River, 9.7-16 mBq/L in the Nanokazawa river, and ND-3.2 mBq/L in the Nuno River. In the poster, we will also present the results of SS measurements and flow observations.
Putra, D.*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Tomihara, Seiichi*; Watanabe, Shun*; Nagao, Seiya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hagiwara, Hiroki; Konishi, Hiromi*
no journal, ,
Identification of radiocesium sorbed minerals in sediments is important in view of adsorbed or desorbed mechanism between minerals and radiocesium in river water. Recently, the authors reported that not only micas but also mafic minerals could contribute toward the radiocesium migration in Fukushima river basin. In this study, we investigated crystal structure of hornblende in riverbed of mafic minerals using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) within Tomioka river. The results showed a part of surface on hornblende is altered to clay minerals. We also confirmed hornblende had cleavages and fractures which filling altered minerals inner part. This implies that these altered minerals could be contribute radiocesium adsorbing.
Aono, Tatsuo*; Nakanishi, Takahiro
no journal, ,
In order to elucidate the distribution, behavior and runoff process of radiocaesium in stream water collected from forest catchments, the activity concentrations of dissolved and particulate radiocaesium were monitored in this area. Although there is a very strong correlation between annual mean activity concentration of dissolved Cs-137 and mean air does rate in catchment area, no features were found with activity concentrations of particulate Cs-137 and mean air does rate in the area. The river water increased due to heavy rains caused by two typhoons in October 2019, and then the topography changed drastically with the inflow of sediment. The radioactivity concentrations of dissolved Cs-137 were decreased by about 50% compared to before the heavy rain. However, the change of radioactivity concentrations of particulate Cs-137 have not been observed. It is considered that the condition of the forest basin has changed as one of reasons.